R graphics
Data Visualisation with R

Graphics 🖼️
- Graphics are commonly stored in a standard image format such as svg, jpg (or jpeg), png, pdf, and so on.
- When you view these graphics electronically, you would be using some graphical device to render the stored image.
- In R, the graphic is rendered by the graphical engine,
grDevices(one of the core R package).
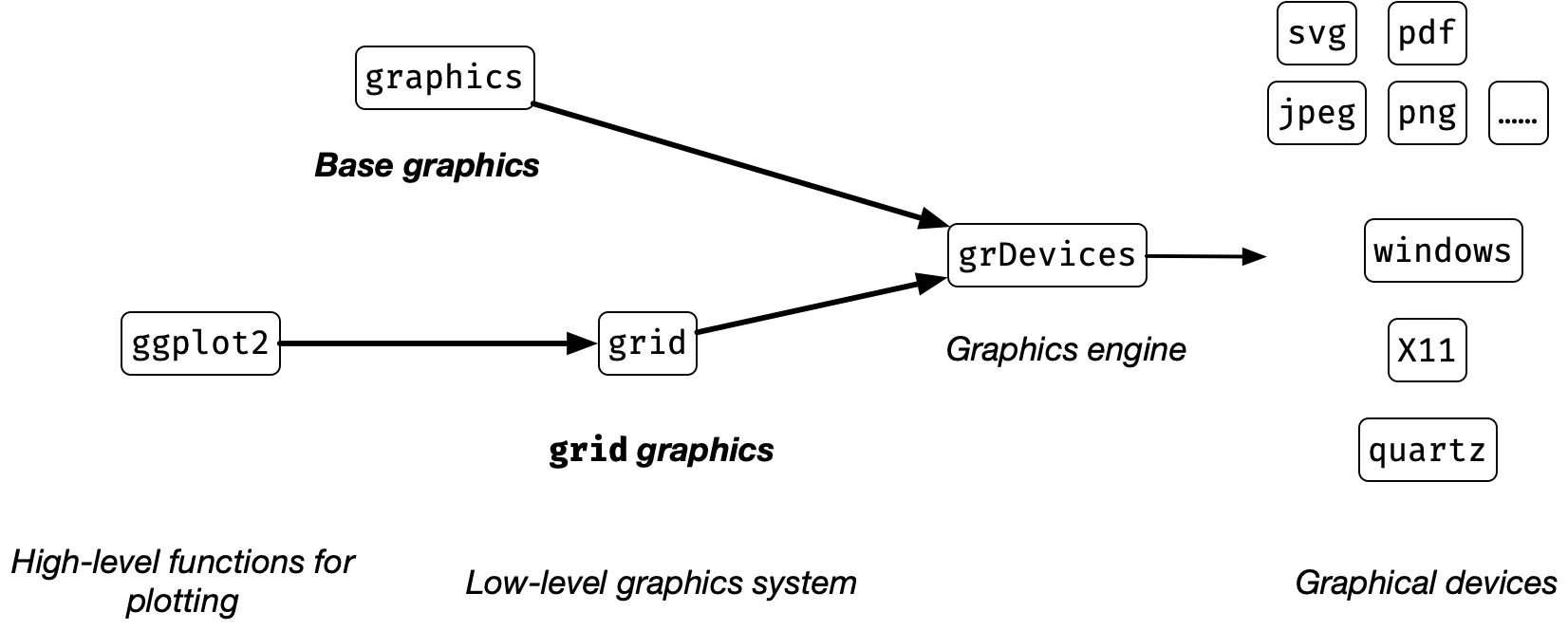
Graphics model in R
- Two main graphics model in R are implemented via two core packages:
graphicspackage, andgridpackage.
- Plot using the
graphicssystem is normally referred to as the base graphics. - If the graphics is produced using the
gridpackage, then it is using thegridgraphics model.
Base graphics
- Base graphics are drawn via the
graphicspackage and shown in display via thegrDevicespackage
grid graphics
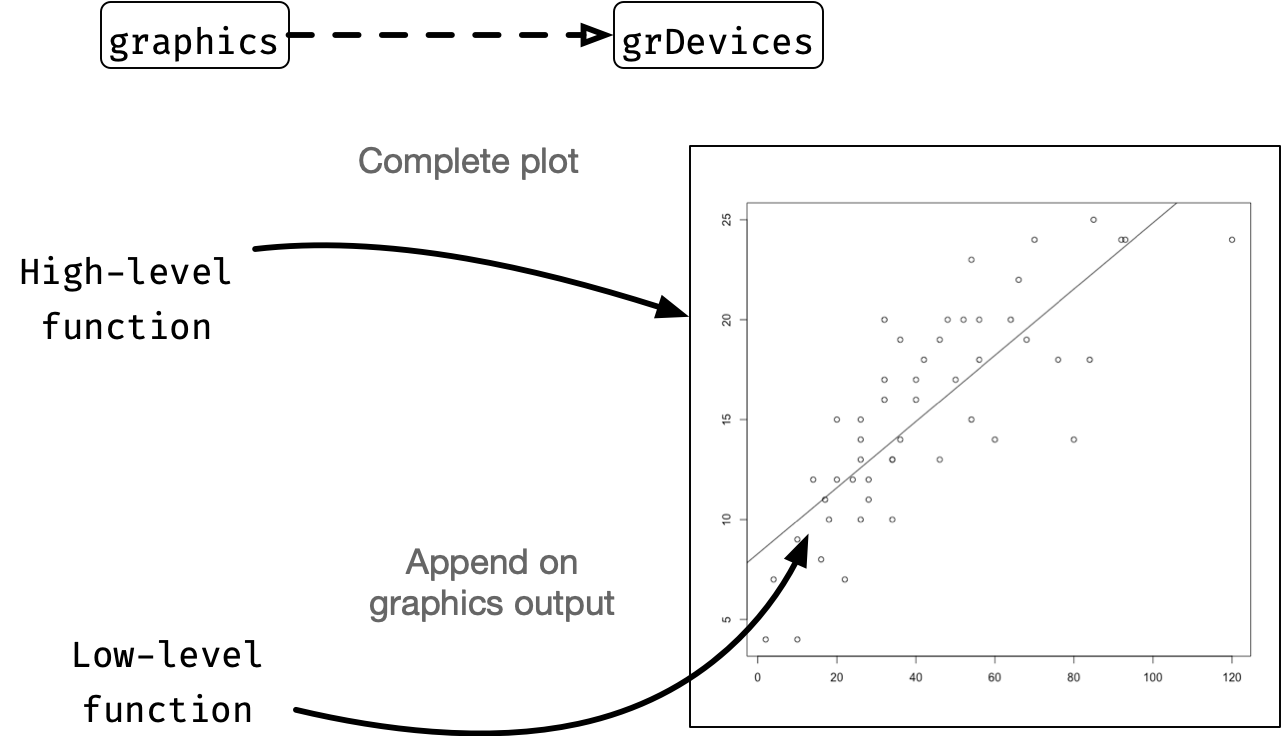
- The
gridpackage contains low-level functions, i.e. draws only parts of the plot. - This system gives a lot of control over the graphics, but requires the user to do a lot of work to draw a complete plot.
- You won’t be directly interacting with the
gridpackage. - Instead you’ll be using the
ggplot2package that provides high-level functions for plotting via thegridsystem.
Other graphical systems
- All other graphical systems are provided via contributed packages (i.e. you need to install it once to use it).
- The two most well known packages are:
latticeandggplot2.
- Both of these packages use the
gridpackage to draw the plots.
Summary of R graphics